What is an API and how can it help Businesses?

The Web is full of examples, definitions, and explanations of “what is an API “. Some of them are funny and very effective, like the following infographic found on Twitter.
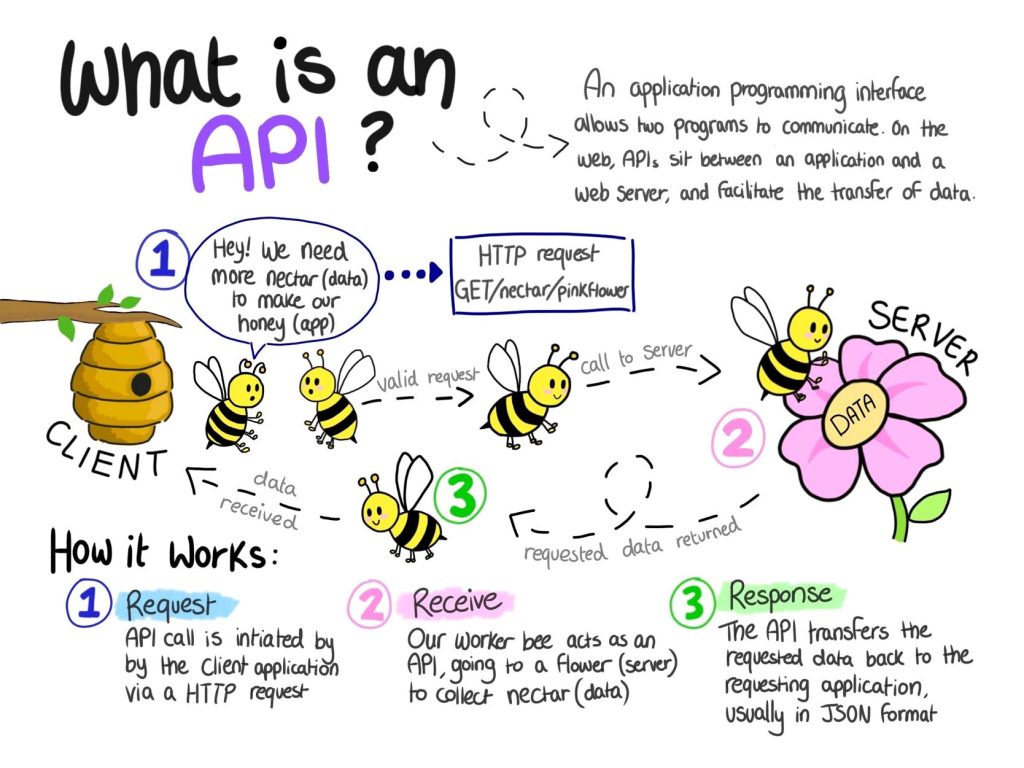
Many are also coming from authoritative voices, like the one of IBM that faced this topic in a very exhaustive and clear way: “An , application programming interface, or API, enables companies to open up their applications’ data and functionality to external third-party developers, business partners, and internal departments within their companies. This allows services and products to communicate with each other and leverage each other’s data and functionality through a documented interface. Developers don’t need to know how an API is implemented; they simply use the interface to communicate with other products and services.”
From a business perspective, the APIs are the foundation of new business models, and they support business growth. By Using APIs, companies can create partnership ecosystems and an open innovation environment, to support the creation of new value streams and innovative services.
Using an API, for businesses, means simplifying processes:
- Improving the workflow, through integration between different tools and applications
- Making it easier to innovate by connecting with new business partners
- Assuring more security through an added layer of protection between data and a server
d-one’ API layer
d-one‘ strategic approach is to enable a fully connected way of making things.
In this perspective d-one is not an alternative to ERP, but a compatible and integrated “add-on” with additional features, able to fit better the customer expectation & requirements.
Digitalsoft’s d-one platform is fully based on API to guarantee full integration with the enterprise ecosystem: ERP, PLM, and any other legacy application already in use in the company.
Through Rest-APIs we enable the dialogue among:
- d-one frontend (Web app, Mobile App, Visual Boards) and d-one backend (Platform Business Logic, Server)
- d-one & external systems (ERP, CRM, other WMS, etc.)
- d-one & external devices (AGV, Robot, forklift, etc.)
in this way, we can easily exchange different kinds of data such as produced quantity, scraps, machine status and changes, downtimes, sensor values, Robot piloting as well as information from ERP like good receipt, material movements, customer orders, and Master data.